Form of separation: FUNCTIONAL
Infrastructure: OPEN EIR
Retail: EIR
Equivalence of access obbligation: EoI and EoO
Supervisory committee: YES
Ireland's Functional separation
- Functional separation (2018): A settlement with the NRA following several legal proceedings. open eir established as the wholesale unit of incumbent eir providing access services to both its retail arm and ANOs, with physically separated staff, own systems, processes and incentives scheme
- Independent Oversight Body (IOB): A five-member committee, with three members appointed by the NRA, established on 24 May 2019. Monitors compliance with non- discrimination and transparency obligations, and regulatory obligations in general.
- Elements of equivalence EoO: M3a/2014 (ex. VULA) - EoI: M3b/2014 and only for VULA in M3a/2014
Key facts
- Fixed broadband subscriptions by technology: xDSL – 62%, FTTH/B – 8%, cable – 26%, FWA – 4%
- Incumbent’s retail broadband market share: Overall 32% – EU average 40% - xDSL 45% - EU average 53%
- Main wholesale competitor: SIRO (a wholesale-only joint venture between Vodafone and ESB)
- Major retail competitor: Virgin Media, Vodafone and Sky
Model of separation adopted
Ireland applies a form of functional separation, resulting from an agreement between the incumbent and the regulator to settle some disputes concerning alleged discriminatory behaviour. open eir, the wholesale unit of the Irish incumbent eir, provides access services to both its retail arm and also to ANOs. Wholesale staff are separated from staff working in eir’s retail arm. There is also separation, for the most part, between wholesale and retail systems and processes, although there is shared but controlled access to certain “low risk” IT systems from both parts of eir’s business.
Organisational and governance structure
In December 2018, eir reached an agreement with ComReg, the telecoms regulator, to:
- create an independent oversight body (IOB) responsible for the compliance of eir’s regulatory obligations;
- increase the independence and transparency of its wholesale unit, open eir;
- establish a new regulatory governance model (RGM) to ensure its future compliance with wholesale non-discrimination and transparency obligations; and
- establish and maintain a regulatory code of practice.
The agreement arose as a compromise between the regulator and eir to settle two separate sets of proceedings raised by ComReg. In these proceedings, eir was charged with five incidences of alleged non-compliance with wholesale obligations, and an additional nine ongoing compliance cases.
The IOB, a new body with supervision responsibilities that will monitor Eir’s compliance with the governance commitments, was established on 24 May 2019. It will also ensure that the incumbent adheres to its regulatory obligations in general, as imposed by ComReg’s decisions.
The IOB, with a majority of independent members, will be a committee jointly established by ComReg and eir. It will consist of five members, with three members, including the chairperson, being appointed by ComReg, while the remaining members will come from eir’s Board. The body will remain in place for five years. Upon termination of the IOB’s term, eir will be entitled to replace the IOB with a committee comprising some or all of the executive or non- executive directors of eir to monitor compliance with regulatory matters.
eir must ensure that the IOB has sufficient resources to commission reviews into the activities of the regulatory governance model. However, eir may refuse such funding if it deems that an external review is unnecessary, providing its reasoning to ComReg. If this were to happen, ComReg may itself then choose to fund the external review.
A summary of IOB’s main responsibilities is provided below:
|
Powers |
Responsibilities |
|
Supervise |
|
|
Recommend |
Propose to eir’s Board any changes to the regulatory governance structure that would impact eir’s ability to meet its regulatory obligations. |
|
Review |
|
|
Report |
|
To increase the operational independence of its wholesale services, Eir will create a wholesale senior management team and a separate wholesale pricing function. The new units will guarantee that the wholesale function operates independently from Eir’s retail arm, treating all wholesale customers in a non-discriminatory manner.
The wholesale senior management team will be responsible for:
- operational decisions
- capex allocation to the wholesale function;
- wholesale access requests and the development of the products that are regulated;
- setting the price for and providing active and passive regulatory access products;
- handling regulated confidential information with other business units; and
- addressing regulatory matters, including compliance with regulatory obligations.
Personnel working in the wholesale function will be located separately from non-wholesale staff. All remuneration incentives for employees in the wholesale function will reflect the achievements solely of the wholesale unit, i.e. will not be based on Eir’s overall performance.
However, the wholesale function will not be a separate legal entity, and overall strategic decisions will continue to be set at Group level in accordance with the decisions made by eir’s Board.
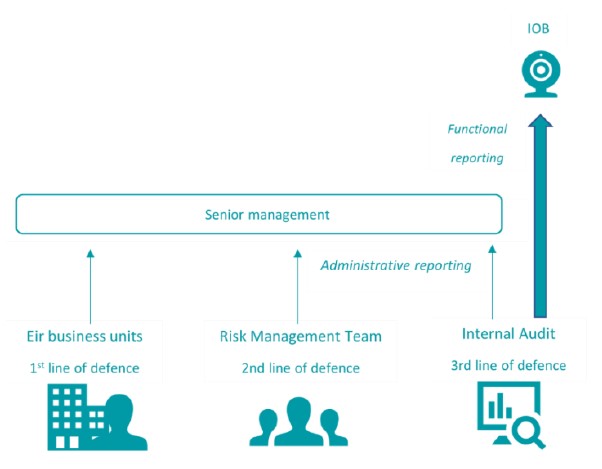
In addition, the incumbent will implement a regulatory governance model (RGM), a new risk management process to ensure the incumbent’s compliance with its regulatory obligations. The enhanced RGM will be based on three levels of risk management as follows:
- First, the business units will manage regulatory risks and assess the compliance of eir’s products with the incumbent’s regulatory obligations.
- Secondly, eir must introduce a risk management team to ensure that the business units have properly assessed the regulatory risk. The risk management team will be independent of the business units and will report to internal audit.
- Thirdly, eir will create an internal audit function to assess that eir’s processes and controls will in fact ensure regulatory compliance.
Each unit will be independent, while the head of internal audit will report directly to the IOB.
Eir’s RGM and reporting system (Cullen International)
In the monitoring of eir’s adherence to the RGM undertakings, IOB takes into account the guiding principles covering:
- bespoke bids processes - evaluation teams for bespoke bids shall include wholesale pricing and risk management function;
- KPIs processes - rules for collection, processing and interpretation of raw data for KPIs;
- Non-operational decision making and approval processes - implement controls to mitigate risk of regulatory conflicts of interests during pre-meeting, post-meeting, distribution of confidential regulated information, etc.; and
- reporting to the IOB – including RGM committee reporting and internal audit reporting.
ComReg regularly reviews eir's implementation of the performance milestones from the settlement agreement. In recognition of the measures implemented by eir so far, ComReg agreed to repay to eir €6.5m from the escrow account.
To facilitate the dialogue on regulated access products between Eir and access seekers, ComReg established an independently chaired Industry Engagement Forum (IEF). It will meet monthly, starting from January 2021.
Elements of equivalence and non-discrimination
Eir will ensure as far as reasonably practicable the independence of the wholesale function. Independence in this context means that the wholesale function operates separately from eir's retail arm, treating all its wholesale customers in a non-discriminatory manner.
Following ComReg's recent market analysis of 2018 and its decision on the pricing of wholesale broadband services, eir provides access in market 3a based on EoO, but must assure access on EoI for VULA (referred to as VUA in Ireland) and civil engineering infrastructure (CEI), such as for pre-ordering, ordering, provisioning, fault logging and repair.
In market 3b, eir is obliged to provide access for bitstream over copper and FTTx (including bitstream provided using upstream WLA inputs) based on EoI.
EoI for CEI provides greater assurances to access seekers that there is no discrimination in the provision of CEI access compared to previously applied EoO model.
Primary changes required to implement EoI solution for CEI relate to the order management system. Order acceptance and acknowledgement could be implemented on eir’s order management and fault handling system unified gateway. In ComReg’s view, eir should make further steps to assure EoI for CEI by aligning access seeker interactions with eir self-supply of CEI.
ComReg considered the transition to EoI for CEI not overly burdensome and the imposition of an obligation of EoI for CEI proportionate. CEI principles were also included in the settlement agreement of December 2018 (Annex 4).